【规划】单纯形法
求解线性规划的单纯形法(这玩意不是都能网络流写的吗(谁跟你这样说的
首先是线性规划的定义
利用松弛变量将约束中的不等式换成等式,则得到
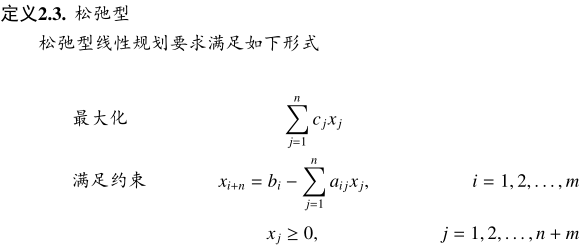
在约束等式左边的 x[n+1]…x[n+m] 叫做基变量,等式右边的 x[1]…x[n] 叫做非基变量
线性规划有三种情况:有解、无解(不存在一个满足限制条件的解)、无界(目标函数可以无穷大)
显然当 bi 非负时令所有基变量为 bi,非基变量为0,即可得到一个满足条件的初始解
有个重要的操作叫转轴(Pivot)
我们可以把一个基变量 x[b] 和非基变量 x[n] 互换,用 x[b] 和其他非基变量代换这个 x[n],这样 x[b] 就成了非基变量,而 x[n] 成了基变量
为了最大化目标函数,我们考虑不停地找一个系数为正的非基变量,然后增大这个量
最优化的具体过程:

举个栗子:
找到 x1,然后限制一为 x1≤30,限制二为 x1≤12,限制三为 x1≤9,所以我们用 x1 代换下界最紧的 x6
得到下面的新线性规划:
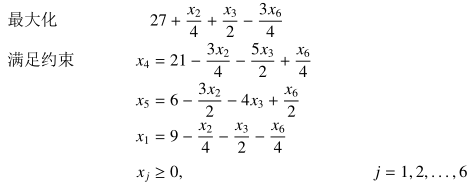
然后找到 x3,得到:
增大 x2 得到
最后得到最大值为28,此时 x1=8, x2=4, x3=0
但是,在 bi 为负的时候,把所有基变量设为0不是一组合法的初始解
我们选择一个 bi 为负的基变量 x[i+n],然后我们在该约束右边找一个系数为正的非基变量,然后进行转轴操作,如果没有系数为正显然就无解了
时间复杂度的话 Pivot 操作的复杂度为 O(nm),但是最优化操作中 Pivot 操作的调用次数可能会成为指数级
其他多项式时间算法:
椭球算法 O(n6m2)
内点算法 O(n3.5m2)
改进的内点算法 O(n3.5m)
例题:UOJ #179. 线性规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 | #include <cstdio>#include <algorithm>#define rep(i, l, r) for(int i=l; i<=r; i++) using namespace std;inline int read(){ int x=0; bool f=0; char ch=getchar(); while (ch<'0' || '9'<ch) f|=ch=='-', ch=getchar(); while ('0'<=ch && ch<='9') x=x*10+ch-'0', ch=getchar(); return f?-x:x;}#define maxn 21#define eps 1e-8int n, m, op, tot, q[maxn], idx[maxn], idy[maxn]; double a[maxn][maxn], A[maxn];inline void Pivot(int x, int y){ swap(idy[x],idx[y]); double tmp=a[x][y]; a[x][y]=1/a[x][y]; rep(i, 0, n) if (y!=i) a[x][i]/=tmp; tot=0; rep(i, 0, n) if (i!=y && (a[x][i]>eps || a[x][i]<-eps)) q[++tot]=i; rep(i, 0, m) { if ((x==i) || (a[i][y]<eps && a[i][y]>-eps)) continue; rep(j, 1, tot) a[i][q[j]]-=a[x][q[j]]*a[i][y]; a[i][y]=-a[i][y]/tmp; }}int main(){ n=read(), m=read(), op=read(); rep(i, 1, n) a[0][i]=read(); rep(i, 1, m) { rep(j, 1, n) a[i][j]=read(); a[i][0]=read(); } rep(i, 1, n) idx[i]=i; rep(i, 1, m) idy[i]=i+n; while (true) { int x=0, y=0; rep(i, 1, m) if (a[i][0]<-eps && ((!x)||(rand()&1))) x=i; if (!x) break; rep(i, 1, n) if (a[x][i]<-eps && ((!y)||(rand()&1))) y=i; if (!y) return puts("Infeasible"),0; Pivot(x,y); } while (true) { int x=0, y=0; double mn=1e15; rep(i, 1, n) if (a[0][i]>eps) {y=i; break;} if (!y) break; rep(i, 1, m) if (a[i][y]>eps && a[i][0]/a[i][y]<mn) mn=a[i][0]/a[i][y], x=i; if (!x) return puts("Unbounded"),0; Pivot(x,y); } printf("%.8lf\n", -a[0][0]); if (!op) return 0; rep(i, 1, m) if (idy[i]<=n) A[idy[i]]=a[i][0]; rep(i, 1, n) printf("%.8lf%c", A[i], i==n?'\n':' '); return 0;} |
其余科学阅读资料:

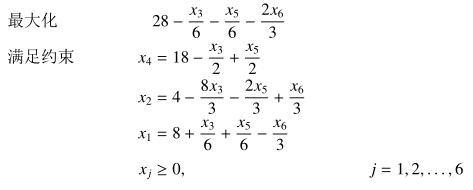
 评论 (0)
评论 (0)